Concept
Docker Engine
分三層
- Server (Docker Deamon):創建/管理 Docker Objects(使用的 images、containers、networks ⋯ 等)。
- REST API:聯繫 Client 及 Server。
- Docker Client:docker CLI;REST API 與內部的 Deamon 互動。
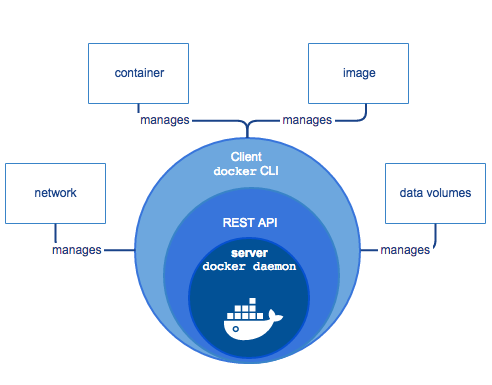
Docker Client 及 Deamon 不需部署在同一台機器上,可以透過遠端遙控其他機器上的 Deamon。
Docker Objects
Images
是個唯獨範本/草稿/藍圖/映像檔(read-only template),用來建立 Docker Container 所需的。
-
Image 內可以引用其他的 Image,例如:
you may build an image which is based on the
ubuntuimage, but installs the Apache web server and your application, as well as the configuration details needed to make your application run. -
可以透過創建 Dockerfile 打造自己的 Image:
Each instruction in a Dockerfile creates a layer in the image. When you change the Dockerfile and rebuild the image, only those layers which have changed are rebuilt. This is part of what makes images so lightweight, small, and fast, when compared to other virtualization technologies.
Containers
是個 Image 的實例(runnable instance of an image),可透過 CLI 控制。
- 相對獨立/孤立於其他 Container 及運行環境。
- Container 內部的環境由 Image 及創建時提供的設定來定義。
- 是個 process runtime。
- 具有獨立的檔案系統(file system)。
Service
Services allow you to scale containers across multiple Docker daemons, which all work together as a swarm with multiple managers and workers. Each member of a swarm is a Docker daemon, and all the daemons communicate using the Docker API. A service allows you to define the desired state, such as the number of replicas of the service that must be available at any given time. By default, the service is load-balanced across all worker nodes. To the consumer, the Docker service appears to be a single application. Docker Engine supports swarm mode in Docker 1.12 and higher.
Container vs VM
| Container | VM |
|---|---|
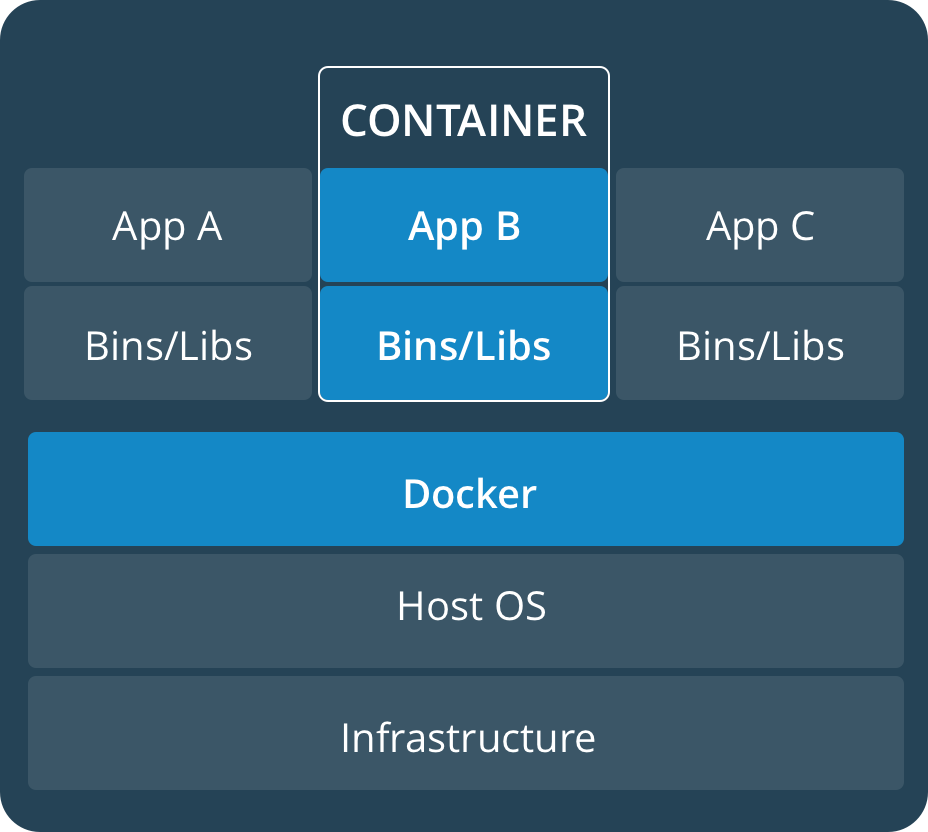 | 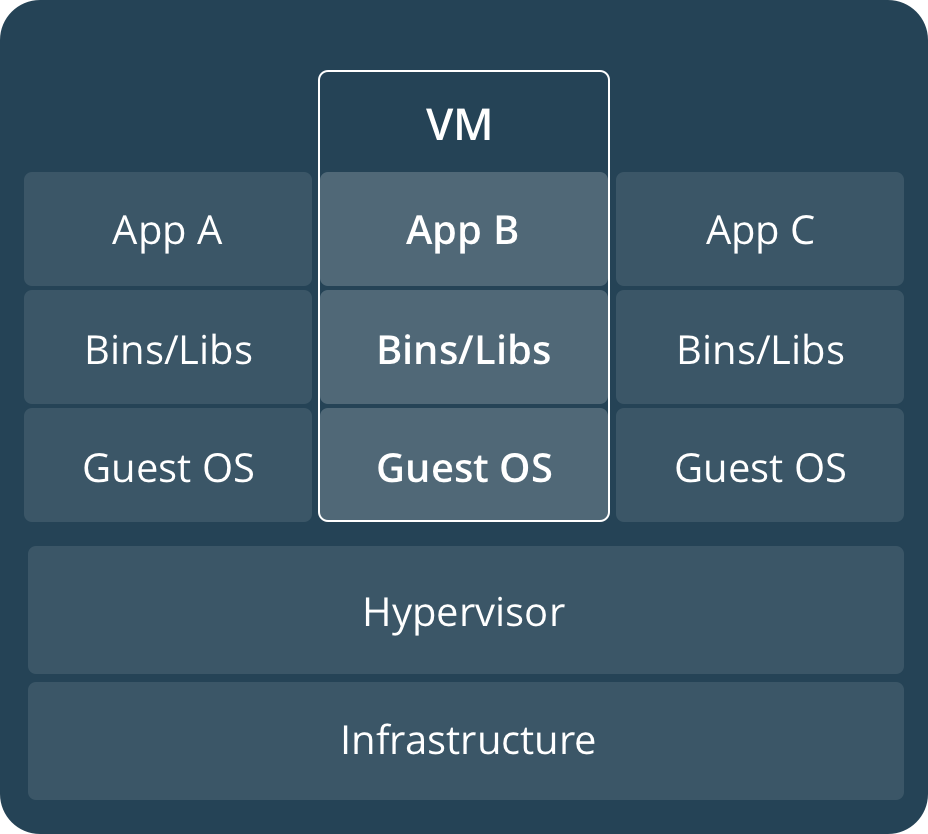 |
| A container runs natively on Linux and shares the kernel of the host machine with other containers. |